What Should Us Note When Using the Head
Upload Time:
Jan 14, 2025
Carbon steel heads will crack in environments such as nitrates, ammonia, and alkaline sodium.
Points to note when using the head:
Austenitic stainless steel will undergo stress corrosion cracking in a specific environment with chloride ions. Please choose the appropriate material when designing.
Carbon steel containers that require hot-dip galvanizing or aluminizing should be heat treated first to remove residual stress.
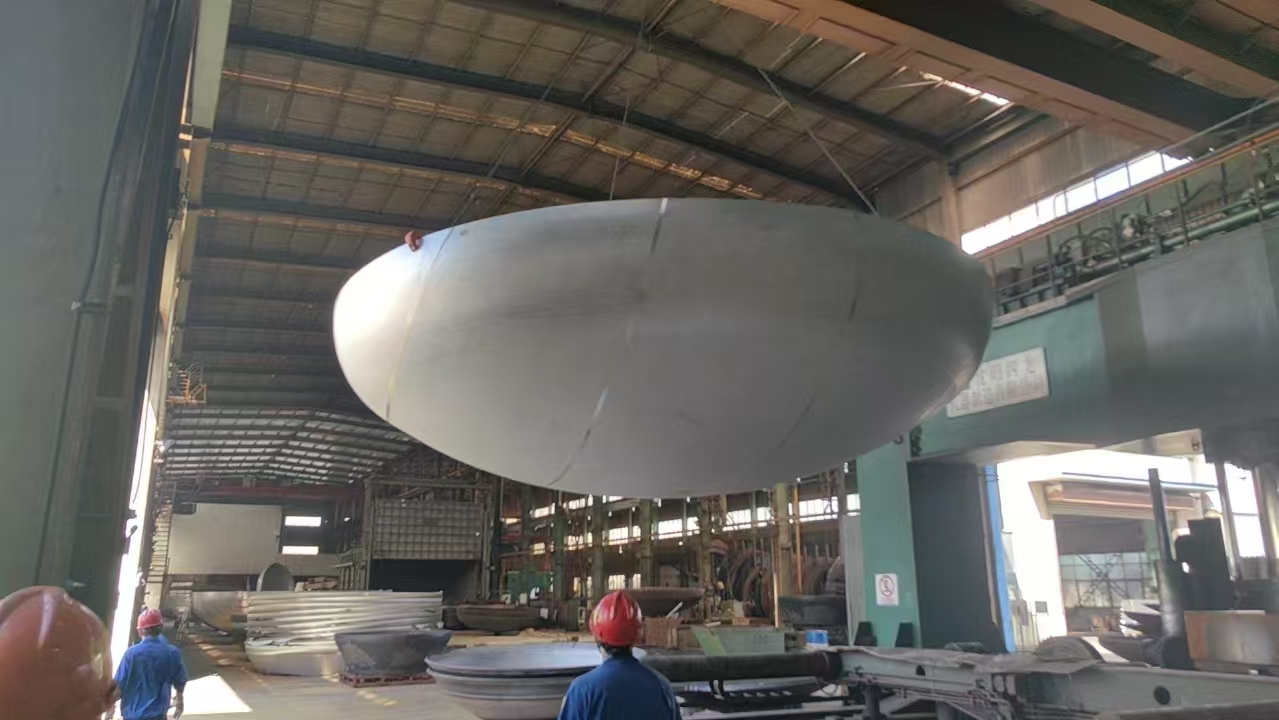

1. Please measure the outer circumference of the head. If the cylinder is processed in advance, please ask the company for the size of the predetermined outer circumference.
2. Please divide the outer circumference of the head into 4 equal parts and mark it on the cylinder and the head.
3. Perform positioning welding. The positioning point of the positioning welding is for the customer to select the position according to the diameter and plate thickness.
4. After the positioning welding is completed, weld. Pay attention to the protection of the surface of the stainless steel head. After the head and the cylinder are welded, the weld seam, heat-affected zone and surrounding welding slag, splash, and pollutants should be cleaned in time, and PT inspection and surface pickling should be performed.
5. Prevent the surface of the stainless steel head from being bumped and scratched.
6. Prevent direct contact with carbon steel to avoid iron ion contamination.
7. Do not store in the open air and prevent rain.
8. Avoid forced welding. The structural design should prevent excessive restraint stress.
9. The chloride ion content of the water used for the water pressure test shall not be greater than 25mg/L, and it should be blown dry in time after the test.
10. Hydrochloric acid and other reducing acids cannot be used for stainless steel pickling.
11. Strictly comply with the medium compatibility specified in the "Container Regulations".
For metastable austenitic stainless steel heads such as 0Cr18Ni9 and 304, it is easy to cause surface pitting corrosion due to improper surface protection. When combined with processing stress and welding stress, it will eventually lead to stress corrosion and intergranular corrosion. For this reason, customers are requested to pay special attention to the surface protection of such stainless steel.
Relevant News